Python Speech to Text with VocaFuse
Adding speech-to-text to your Python app usually means wrestling with audio preprocessing, managing Whisper containers, and building webhook infrastructure. Here's the fast path:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
from vocafuse import AccessToken
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/api/vocafuse-token', methods=['POST'])
def generate_token():
token = AccessToken(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET'],
identity='user_123'
)
return jsonify(token())
That's your Python backend generating secure tokens for frontend audio capture. This guide covers how speech to text APIs work, complete Flask and FastAPI implementations, webhook handling, and production patterns. Code first, theory later.
What is a Speech to Text API?
A speech to text API converts audio files or streams into written text using cloud-based machine learning models. Instead of deploying and maintaining your own transcription infrastructure, you send audio to a service and receive text back.
How to Build Speech to Text in Python
With VocaFuse, your Python backend is one piece of a larger system. Here's the architecture:
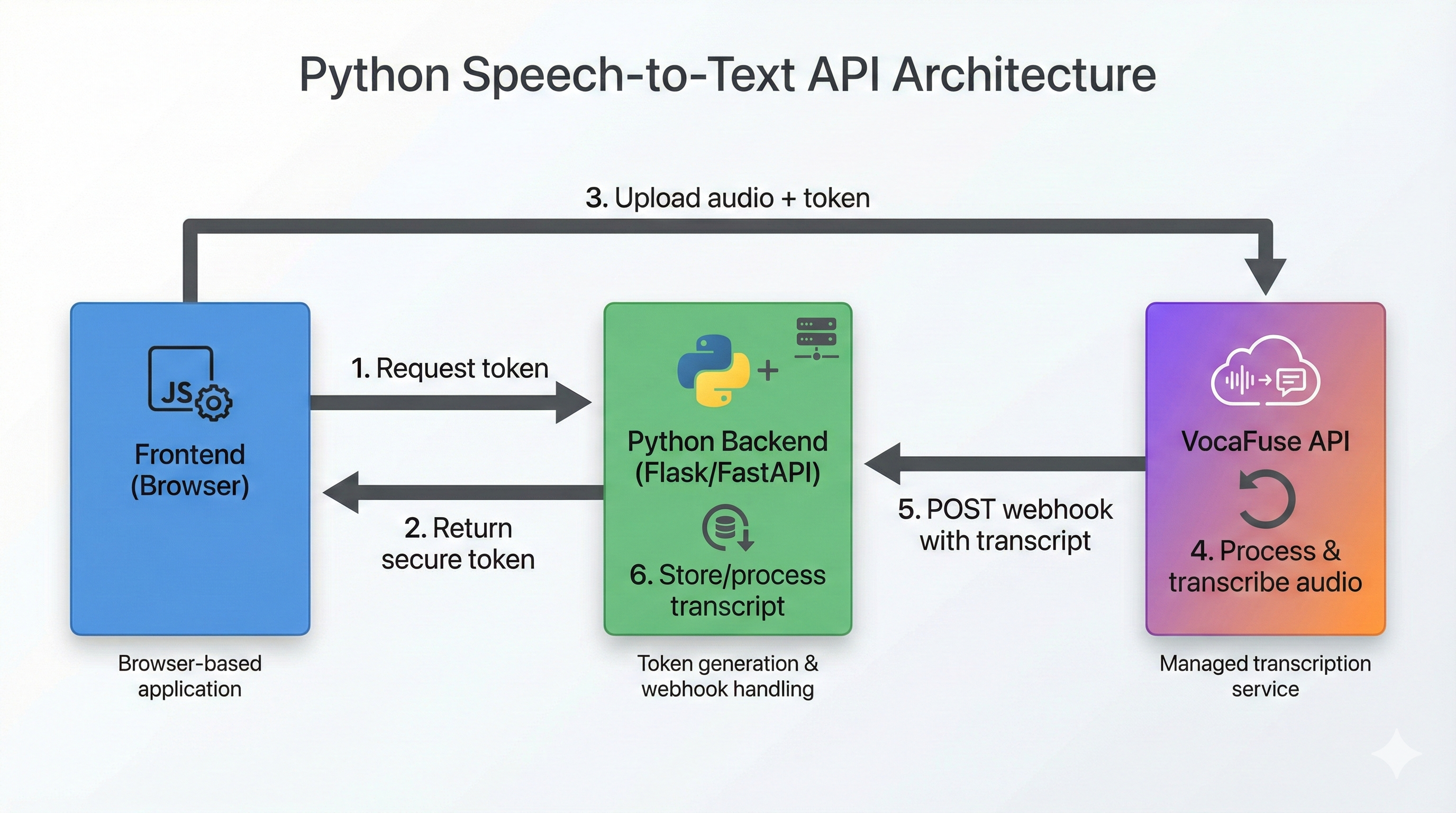
Here's the full flow:
- Frontend (JavaScript SDK): Captures audio in the browser
- Your Python Backend: Issues JWT tokens to frontend (keeps API keys secure)
- Frontend → VocaFuse: Uploads audio directly using the token
- VocaFuse: Processes audio via OpenAI Whisper, generates transcript
- VocaFuse → Your Python Backend: Sends webhook on completion
- Your Python Backend: Receives webhook, processes/stores transcript ID
Your Python backend provides:
- Token generation endpoint (security layer)
- Webhook receiver (business logic, storage)
- Optional: Transcript retrieval API for your frontend
The VocaFuse JavaScript SDK handles:
- Cross-browser audio recording
- Direct upload to VocaFuse
- See VocaFuse JavaScript Voice Recording SDK for full implementation
VocaFuse provides:
- Secure file upload with presigned URLs
- S3 storage with lifecycle policies
- Queue management and dead-letter handling
- Webhook delivery with HMAC signatures and retries
- Multi-tenant authentication and rate limiting
- Error monitoring and alerting
Minimal Frontend Setup (Prerequisite)
Your Python backend requires a frontend to capture audio. Here's the minimal JavaScript needed:
Step 1: Install the SDK
npm install vocafuse
Step 2: Initialize with your Python token endpoint
import { VocaFuseSDK } from 'vocafuse';
const sdk = new VocaFuseSDK({ tokenEndpoint: '/api/vocafuse-token' });
await sdk.init();
const recorder = sdk.createRecorder({
maxDuration: 60,
onComplete: (result) => console.log('Uploaded:', result.recording_id)
});
// Start recording
await recorder.start();
// Stop and upload
await recorder.stop();
That's all you need for frontend setup. For production features (error handling, React/Vue integration, streaming), see the complete JavaScript SDK documentation.
The rest of this guide focuses on building your Python backend.
Quick Start: Python Backend for Speech to Text
Here's a minimal Flask backend with token generation and webhook handling:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from vocafuse import AccessToken, RequestValidator
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/api/vocafuse-token', methods=['POST'])
def generate_token():
user_id = get_current_user_id() # Your auth logic
token = AccessToken(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET'],
identity=str(user_id)
)
return jsonify(token())
validator = RequestValidator(os.environ['VOCAFUSE_WEBHOOK_SECRET'])
@app.route('/api/webhooks/vocafuse', methods=['POST'])
def handle_webhook():
payload = request.get_data(as_text=True)
signature = request.headers.get('X-VocaFuse-Signature')
if not validator.validate(payload, signature):
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid signature'}), 401
data = request.get_json()
if data['event'] == 'recording.transcribed':
text = data['recording']['transcription']['text']
print(f"Transcription: {text}")
# Save to database, trigger workflows, etc.
return jsonify({'status': 'received'}), 200
Run it with flask run and you have a working speech to text Python backend.
Python SDK Setup and Authentication
Installation
pip install vocafuse
Or add to requirements.txt:
vocafuse>=1.0.0
Environment Variables
Create a .env file (never commit this):
VOCAFUSE_API_KEY=sk_live_your_api_key_here
VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET=your_api_secret_here
VOCAFUSE_WEBHOOK_SECRET=your_webhook_secret_here
Get your keys from the VocaFuse dashboard.
Client Initialization
For operations like fetching transcripts or managing webhooks:
from vocafuse import Client
import os
client = Client(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET']
)
# Test connection by listing recordings
recordings = client.recordings.list(limit=5)
print(f"Found {len(recordings)} recordings")
For advanced configuration (timeouts, retries, debug logging), see SDK Configuration.
Token Generation
For frontend authentication, use AccessToken:
from vocafuse import AccessToken
token = AccessToken(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET'],
identity='user_12345' # Your user identifier
)
result = token(expires_in=3600) # 1 hour expiry
print(result['token'])
The identity parameter ties uploads to specific users—useful for multi-tenant apps.
Handling Transcription Webhooks
Webhooks are how VocaFuse notifies your backend when transcription completes. This is the core of your Python integration.
Webhook Payload Structure
When transcription succeeds (recording.transcribed):
{
"event": "recording.transcribed",
"timestamp": 1703001600,
"recording": {
"id": "rec_1234567890",
"identity": "user_12345",
"status": "completed",
"duration": 45.2,
"created_at": 1703001500,
"completed_at": 1703001600,
"transcription": {
"text": "This is the transcribed text from the voice note.",
"confidence": 0.985,
"language": "en"
}
}
}
When transcription fails (recording.failed):
{
"event": "recording.failed",
"timestamp": 1703001600,
"recording": {
"id": "rec_1234567890",
"identity": "user_12345",
"status": "failed",
"created_at": 1703001500
},
"error": {
"code": "TRANSCRIPTION_FAILED",
"message": "Audio quality too low for transcription"
}
}
Signature Verification
Always verify webhook signatures before processing. This prevents attackers from sending fake webhooks:
from vocafuse import RequestValidator
validator = RequestValidator(os.environ['VOCAFUSE_WEBHOOK_SECRET'])
@app.route('/api/webhooks/vocafuse', methods=['POST'])
def handle_webhook():
# Use raw payload, not parsed JSON
payload = request.get_data(as_text=True)
signature = request.headers.get('X-VocaFuse-Signature')
if not validator.validate(payload, signature):
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid signature'}), 401
# Safe to process
data = request.get_json()
# ...
Don't use json.dumps(request.get_json()) for the payload—that modifies whitespace and breaks signature validation. Always use the raw payload.
Flask Backend Implementation
Here's a complete Flask application for Python speech to text:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from vocafuse import Client, AccessToken, RequestValidator
import os
import logging
app = Flask(__name__)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# Initialize SDK
client = Client(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET']
)
validator = RequestValidator(os.environ['VOCAFUSE_WEBHOOK_SECRET'])
@app.route('/api/vocafuse-token', methods=['POST'])
def generate_token():
"""Generate JWT token for frontend SDK authentication."""
user_id = get_current_user_id() # Your auth logic
token = AccessToken(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET'],
identity=str(user_id)
)
return jsonify(token())
@app.route('/api/webhooks/vocafuse', methods=['POST'])
def handle_webhook():
"""Receive and process VocaFuse webhook events."""
payload = request.get_data(as_text=True)
signature = request.headers.get('X-VocaFuse-Signature')
if not validator.validate(payload, signature):
logging.warning('Invalid webhook signature')
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid signature'}), 401
data = request.get_json()
event = data['event']
if event == 'recording.transcribed':
handle_transcription_complete(data['recording'])
elif event == 'recording.failed':
handle_transcription_failed(data['recording'], data['error'])
return jsonify({'status': 'received'}), 200
@app.route('/api/transcripts/<recording_id>', methods=['GET'])
def get_transcript(recording_id):
"""Retrieve transcript for a specific recording."""
try:
transcription = client.recordings(recording_id).transcription.get()
return jsonify({
'text': transcription['text'],
'confidence': transcription['confidence'],
'language': transcription['language']
})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 404
def handle_transcription_complete(recording):
"""Process successful transcription."""
logging.info(f"Transcription complete: {recording['id']}")
text = recording['transcription']['text']
user_id = recording['identity']
confidence = recording['transcription']['confidence']
# Save to database
save_to_database(
recording_id=recording['id'],
user_id=user_id,
text=text,
confidence=confidence
)
# Trigger downstream workflows
# notify_user(user_id, recording['id'])
def handle_transcription_failed(recording, error):
"""Handle failed transcription."""
logging.error(f"Transcription failed: {recording['id']} - {error['message']}")
# Notify user, log for debugging, etc.
def get_current_user_id():
"""Your authentication logic here."""
# Example: Extract from session, JWT, etc.
return request.headers.get('X-User-ID', 'anonymous')
def save_to_database(recording_id, user_id, text, confidence):
"""Your database logic here."""
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, port=5000)
Running Locally with ngrok
For local webhook testing:
# Terminal 1: Start Flask
python app.py
# Terminal 2: Expose via ngrok
ngrok http 5000
# Use the ngrok URL when registering webhooks
# Example: https://abc123.ngrok.io/api/webhooks/vocafuse
FastAPI Backend Implementation
FastAPI offers async support, automatic OpenAPI docs, and type safety. Here's the equivalent implementation:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, HTTPException, BackgroundTasks
from pydantic import BaseModel
from vocafuse import Client, AccessToken, RequestValidator
import os
import logging
app = FastAPI(title="Voice Notes API")
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# Initialize SDK
client = Client(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET']
)
validator = RequestValidator(os.environ['VOCAFUSE_WEBHOOK_SECRET'])
class TokenResponse(BaseModel):
token: str
class TranscriptResponse(BaseModel):
text: str
confidence: float
language: str
@app.post('/api/vocafuse-token', response_model=TokenResponse)
async def generate_token(request: Request):
"""Generate JWT token for frontend SDK authentication."""
user_id = request.headers.get('X-User-ID', 'anonymous')
token = AccessToken(
api_key=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_KEY'],
api_secret=os.environ['VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET'],
identity=str(user_id)
)
result = token(expires_in=3600)
return TokenResponse(token=result['token'])
@app.post('/api/webhooks/vocafuse')
async def handle_webhook(request: Request, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
"""Receive and process VocaFuse webhook events."""
payload = await request.body()
payload_str = payload.decode('utf-8')
signature = request.headers.get('X-VocaFuse-Signature')
if not validator.validate(payload_str, signature):
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail='Invalid signature')
data = await request.json()
event = data['event']
# Process in background for fast webhook response
if event == 'recording.transcribed':
background_tasks.add_task(process_transcription, data['recording'])
elif event == 'recording.failed':
background_tasks.add_task(process_failure, data['recording'], data['error'])
return {'status': 'received'}
@app.get('/api/transcripts/{recording_id}', response_model=TranscriptResponse)
async def get_transcript(recording_id: str):
"""Retrieve transcript for a specific recording."""
try:
transcription = client.recordings(recording_id).transcription.get()
return TranscriptResponse(
text=transcription['text'],
confidence=transcription['confidence'],
language=transcription['language']
)
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail=str(e))
async def process_transcription(recording: dict):
"""Background task for processing transcription."""
logging.info(f"Processing transcription: {recording['id']}")
# Save to database, send notifications, etc.
async def process_failure(recording: dict, error: dict):
"""Background task for handling failures."""
logging.error(f"Transcription failed: {recording['id']} - {error['message']}")
Run with:
uvicorn app:app --reload --port 5000
FastAPI auto-generates OpenAPI docs at /docs—useful for testing your endpoints.
Working with Transcription Results
When you need the full transcript (not just webhook data), fetch it from the API:
transcription = client.recordings('rec_123').transcription.get()
Response structure:
{
'id': 'b585a2af-56b3-435d-a51c-024d4cccfe0f',
'recording_id': 'rec_123',
'text': 'This is the transcribed text from the audio.',
'confidence': 0.95,
'language': 'english',
'provider': 'openai',
'model': 'whisper-1',
'processing_duration_ms': 1367
}
Common Processing Tasks
Search transcripts:
recordings = client.recordings.list(limit=100)
matches = [v for v in recordings if 'keyword' in v.get('text', '').lower()]
Filter by date range:
recordings = client.recordings.list(
date_from='2025-01-01',
date_to='2025-01-31',
status='transcribed'
)
Format for subtitles: Use the words field (when available) for word-level timestamps.
Production Considerations
Error Handling
from vocafuse import Client, VocaFuseError, AuthenticationError, RateLimitError
try:
recording = client.recordings.get('rec_123')
except AuthenticationError:
# Invalid API credentials
logging.error('Invalid API credentials')
except RateLimitError as e:
# Back off and retry
logging.warning(f'Rate limited. Retry after {e.retry_after} seconds')
except VocaFuseError as e:
# General API error
logging.error(f'API error: {e.message}')
For complete error handling patterns, exception types, and retry configuration, see SDK Configuration.
Webhook Reliability
VocaFuse retries failed webhooks with exponential backoff:
| Attempt | Delay |
|---|---|
| 1 | Immediate |
| 2 | 30 seconds |
| 3 | 5 minutes |
| 4 | 30 minutes |
| 5 | 2 hours |
Handle duplicates with idempotency:
processed_ids = set() # Use Redis/database in production
def process_transcription(recording):
recording_id = recording['id']
if recording_id in processed_ids:
return # Already processed
# Process...
processed_ids.add(recording_id)
What You Don't Build with Managed APIs
- Audio capture and upload infrastructure (frontend SDK handles this)
- Audio preprocessing pipelines (format conversion, sample rate normalization)
- Whisper model deployment and updates
- Multi-tenant isolation
- Webhook delivery infrastructure with retries
Python Voice Transcription: Advanced Features
VocaFuse supports additional features via the API:
Language detection: Automatic—check transcription['language'] in responses.
Custom webhook events: Subscribe to recording.transcribed and recording.failed:
client.webhooks.create(
url='https://your-domain.com/webhooks/vocafuse',
events=['recording.transcribed', 'recording.failed'],
secret='your_webhook_secret'
)
Filtering recordings:
# By status
transcribed = client.recordings.list(status='transcribed')
# By date range
january = client.recordings.list(
date_from='2025-01-01',
date_to='2025-01-31'
)
Comparing Python Speech to Text Options
| Feature | VocaFuse | Google Cloud STT | AWS Transcribe | Self-hosted Whisper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setup time | ~15 min | 30-45 min | 30-45 min | Days |
| Webhook delivery | Built-in | Manual | Manual | Manual |
| Token auth for frontend | Built-in | Manual | Manual | Manual |
| Maintenance | None | Low | Low | High |
| Best for | Fast integration | GCP ecosystem | AWS ecosystem | Full control |
When to use cloud APIs: You want to ship this week, need managed infrastructure, prefer usage-based pricing.
When to self-host: You're processing 10,000+ hours/month, need full control, have ML ops capacity.
Troubleshooting Common Errors
Authentication Failures
AuthenticationError: Invalid API credentials
Fix: Verify VOCAFUSE_API_KEY and VOCAFUSE_API_SECRET are set correctly. Keys start with sk_live_.
Webhook Signature Mismatch
401: Invalid signature
Fix: Use raw payload, not parsed JSON:
# ✅ Correct
payload = request.get_data(as_text=True)
# ❌ Wrong - modifies whitespace
payload = json.dumps(request.get_json())
Webhooks Not Received
Causes:
- Firewall blocking incoming requests
- Incorrect webhook URL
- Local development without ngrok
Fix for local development:
ngrok http 5000
# Register webhook with ngrok URL
Rate Limiting (429 Errors)
except RateLimitError as e:
time.sleep(e.retry_after)
# Retry request
Transcription Not Ready
404: TRANSCRIPTION_NOT_READY
Fix: Use webhooks instead of polling. The transcription endpoint returns 404 while processing is in progress.
Next Steps
Related tutorials:
- JavaScript Speech to Text — Coming soon
- Node.js Speech to Text — Coming soon
Reference documentation:
- SDK Configuration — Timeouts, retries, error handling
- JavaScript SDK — Complete frontend implementation
- Webhooks Guide — Production webhook patterns
- API Reference — Full endpoint documentation
Get Started
Ready to add voice transcription to your Python app?
- Get your API keys (free tier available)
- Copy the Flask or FastAPI example above
- Set up your webhook endpoint
- Test with a voice recording
First transcript in under 15 minutes. No infrastructure to manage.